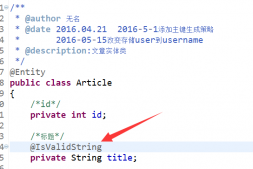
springboot集成RabbitMQ非常簡單,如果只是簡單的使用配置非常少,springboot提供了spring-boot-starter-amqp項目對消息各種支持。
1.新建一個Spring Boot工程,命名為:“rabbitmq-hello”。
在pom.xml中引入如下依賴內容,其中spring-boot-starter-amqp用于支持RabbitMQ。
|
1
2
3
4
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId></dependency> |
2.在application.properties中配置關于RabbitMQ的連接和用戶信息,用戶可以回到上面的安裝內容,在管理頁面中創建用戶。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
spring.application.name=rabbitmq-hellospring.rabbitmq.host=localhostspring.rabbitmq.port=5672spring.rabbitmq.username=adminspring.rabbitmq.password=123456 |
3.創建消息生產者Sender。通過注入AmqpTemplate接口的實例來實現消息的發送,AmqpTemplate接口定義了一套針對AMQP協議的基礎操作。
在Spring Boot中會根據配置來注入其具體實現。在該生產者,我們會產生一個字符串,并發送到名為hello的隊列中。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@Componentpublic class Sender { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate; public void send() { String context = "hello " + new Date(); System.out.println("Sender : " + context); this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("hello", context); }} |
4.創建消息消費者Receiver。
通過@RabbitListener注解定義該類對hello隊列的監聽,并用@RabbitHandler注解來指定對消息的處理方法。所以,該消費者實現了對hello隊列的消費,消費操作為輸出消息的字符串內容。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Component@RabbitListener(queues = "hello")public class Receiver { @RabbitHandler public void process(String hello) { System.out.println("Receiver : " + hello); }} |
5.創建RabbitMQ的配置類RabbitConfig,用來配置隊列、交換器、路由等高級信息。這里我們以入門為主,先以最小化的配置來定義,以完成一個基本的生產和消費過程。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@Configurationpublic class RabbitConfig { @Bean public Queue helloQueue() { return new Queue("hello"); }} |
6.創建應用主類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class HelloApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class, args); }} |
7.創建單元測試類,用來調用消息生產:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)@SpringApplicationConfiguration(classes = HelloApplication.class)public class HelloApplicationTests { @Autowired private Sender sender; @Test public void hello() throws Exception { sender.send(); }} |
8.啟動應用主類,從控制臺中,我們看到如下內容,程序創建了一個訪問127.0.0.1:5672中admin的連接。
|
1
|
o.s.a.r.c.CachingConnectionFactory : Created new connection: SimpleConnection@29836d32 [delegate=amqp://[email protected]:5672/] |
同時,我們通過RabbitMQ的控制面板,可以看到Connection和Channels中包含當前連接的條目。
9.運行單元測試類,我們可以看到控制臺中輸出下面的內容,消息被發送到了RabbitMQ Server的hello隊列中。
Sender : hello Sun Sep 25 11:06:11 CST 2016
10.切換到應用主類的控制臺,我們可以看到類似如下輸出,消費者對hello隊列的監聽程序執行了,并輸出了接受到的消息信息。
|
1
|
Receiver : hello Sun Sep 25 11:06:11 CST 2016 |
通過上面的示例,我們在Spring Boot應用中引入spring-boot-starter-amqp模塊,進行簡單配置就完成了對RabbitMQ的消息生產和消費的開發內容。
需要注意的地方,Direct模式相當于一對一模式,一個消息被發送者發送后,會被轉發到一個綁定的消息隊列中,然后被一個接收者接收!
實際上RabbitMQ還可以支持發送對象:當然由于涉及到序列化和反序列化,該對象要實現Serilizable接口.HelloSender做出如下改寫:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public void send() { User user=new User(); //實現Serializable接口 user.setUsername("hlhdidi"); user.setPassword("123"); template.convertAndSend("queue",user);}HelloReceiver做出如下改寫:@RabbitListener(queues="queue") //監聽器監聽指定的Queuepublic void process1(User user) { //用User作為參數 System.out.println("Receive1:"+user);} |
以上所述是小編給大家介紹的spring boot整合RabbitMQ(Direct模式),希望對大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問請給我留言,小編會及時回復大家的。在此也非常感謝大家對服務器之家網站的支持!
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/web424/p/6763031.html