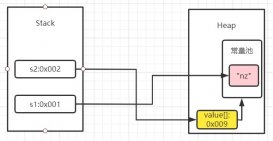
在Java里面,可以用復(fù)制語句”A=B”給基本類型的數(shù)據(jù)傳遞值,但是如果A,B是兩個(gè)同類型的數(shù)組,復(fù)制就相當(dāng)于將一個(gè)數(shù)組變量的引用傳遞給另一個(gè)數(shù)組;如果一個(gè)數(shù)組發(fā)生改變,那么引用同一數(shù)組的變量也要發(fā)生改變。
以下是歸納的 java 中復(fù)制數(shù)組的方法:
(1) 使用FOR循環(huán),將數(shù)組的每個(gè)元素復(fù)制或者復(fù)制指定元素,不過效率差一點(diǎn)
(2) 使用clone方法,得到數(shù)組的值,而不是引用,不能復(fù)制指定元素,靈活性差一點(diǎn)
(3) 使用System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length)方法,推薦使用
舉例:
1.使用FOR循環(huán)
|
1
2
3
|
int[] src={1,3,5,6,7,8};int[] dest = new int[6];for(int i=0;i<6;i++) dest[i] = src[i]; |
2.使用clone
|
1
2
3
|
int[] src={1,3,5,6,7,8};int[] dest;dest=(int[]) src.clone();//使用clone創(chuàng)建 |
副本,注意clone要使用強(qiáng)制轉(zhuǎn)換
3.使用System.arraycopy
|
1
2
3
|
int[] src={1,3,5,6,7,8};int[] dest = new int[6];System.arraycopy(src, 0, dest, 0, 6); |
System提供了一個(gè)靜態(tài)方法arraycopy(),我們可以使用它來實(shí)現(xiàn)數(shù)組之間的復(fù)制。
其函數(shù)原型是:public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
src:源數(shù)組;;srcPos:源數(shù)組要復(fù)制的起始位置;
dest:目的數(shù)組;destPos:目的數(shù)組放置的起始位置;
length:復(fù)制的長度。
注意:src and dest都必須是同類型或者可以進(jìn)行轉(zhuǎn)換類型的數(shù)組。有趣的是這個(gè)函數(shù)可以實(shí)現(xiàn)自己到自己復(fù)制,比如:
|
1
2
|
int[] fun ={0,1,2,3,4,5,6};System.arraycopy(fun,0,fun,3,3); |
則結(jié)果為:{0,1,2,0,1,2,6};
以上介紹的就是Java語言中數(shù)組的幾種復(fù)制方法,希望對大家有所幫助,如果大家有任何疑問請給我留言,小編會及時(shí)回復(fù)大家的。在此也非常感謝大家對服務(wù)器之家網(wǎng)站的支持!
原文鏈接:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_29384657/article/details/51768779