前提
org.springframework.core.env.environment是當(dāng)前應(yīng)用運(yùn)行環(huán)境的公開(kāi)接口,主要包括應(yīng)用程序運(yùn)行環(huán)境的兩個(gè)關(guān)鍵方面:配置文件(profiles)和屬性。environment繼承自接口propertyresolver,而propertyresolver提供了屬性訪問(wèn)的相關(guān)方法。這篇文章從源碼的角度分析environment的存儲(chǔ)容器和加載流程,然后基于源碼的理解給出一個(gè)生產(chǎn)級(jí)別的擴(kuò)展。
本文較長(zhǎng),請(qǐng)用一個(gè)舒服的姿勢(shì)閱讀。
environment類體系

- propertyresolver:提供屬性訪問(wèn)功能。
- configurablepropertyresolver:繼承自propertyresolver,主要提供屬性類型轉(zhuǎn)換(基于org.springframework.core.convert.conversionservice)功能。
- environment:繼承自propertyresolver,提供訪問(wèn)和判斷profiles的功能。
- configurableenvironment:繼承自configurablepropertyresolver和environment,并且提供設(shè)置激活的profile和默認(rèn)的profile的功能。
- configurablewebenvironment:繼承自configurableenvironment,并且提供配置servlet上下文和servlet參數(shù)的功能。
- abstractenvironment:實(shí)現(xiàn)了configurableenvironment接口,默認(rèn)屬性和存儲(chǔ)容器的定義,并且實(shí)現(xiàn)了configurableenvironment種的方法,并且為子類預(yù)留可覆蓋了擴(kuò)展方法。
- standardenvironment:繼承自abstractenvironment,非servlet(web)環(huán)境下的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)environment實(shí)現(xiàn)。
- standardservletenvironment:繼承自standardenvironment,servlet(web)環(huán)境下的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)environment實(shí)現(xiàn)。
reactive相關(guān)的暫時(shí)不研究。
environment提供的方法
一般情況下,我們?cè)趕pringmvc項(xiàng)目中啟用到的是standardservletenvironment,它的父接口問(wèn)configurablewebenvironment,我們可以查看此接口提供的方法:

environment的存儲(chǔ)容器
environment的靜態(tài)屬性和存儲(chǔ)容器都是在abstractenvironment中定義的,configurablewebenvironment接口提供的getpropertysources()方法可以獲取到返回的mutablepropertysources實(shí)例,然后添加額外的propertysource。實(shí)際上,environment的存儲(chǔ)容器就是org.springframework.core.env.propertysource的子類集合,abstractenvironment中使用的實(shí)例是org.springframework.core.env.mutablepropertysources,下面看下propertysource的源碼:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
public abstract class propertysource<t> { protected final log logger = logfactory.getlog(getclass()); protected final string name; protected final t source; public propertysource(string name, t source) { assert.hastext(name, "property source name must contain at least one character"); assert.notnull(source, "property source must not be null"); this.name = name; this.source = source; } @suppresswarnings("unchecked") public propertysource(string name) { this(name, (t) new object()); } public string getname() { return this.name; } public t getsource() { return this.source; } public boolean containsproperty(string name) { return (getproperty(name) != null); } @nullable public abstract object getproperty(string name); @override public boolean equals(object obj) { return (this == obj || (obj instanceof propertysource && objectutils.nullsafeequals(this.name, ((propertysource<?>) obj).name))); } @override public int hashcode() { return objectutils.nullsafehashcode(this.name); } //省略其他方法和內(nèi)部類的源碼 } |
源碼相對(duì)簡(jiǎn)單,預(yù)留了一個(gè)getproperty抽象方法給子類實(shí)現(xiàn),重點(diǎn)需要關(guān)注的是覆寫(xiě)了的equals和hashcode方法,實(shí)際上只和name屬性相關(guān),這一點(diǎn)很重要,說(shuō)明一個(gè)propertysource實(shí)例綁定到一個(gè)唯一的name,這個(gè)name有點(diǎn)像hashmap里面的key,部分移除、判斷方法都是基于name屬性。propertysource的最常用子類是mappropertysource、propertiespropertysource、resourcepropertysource、stubpropertysource、comparisonpropertysource:
- mappropertysource:source指定為map實(shí)例的propertysource實(shí)現(xiàn)。
- propertiespropertysource:source指定為map實(shí)例的propertysource實(shí)現(xiàn),內(nèi)部的map實(shí)例由properties實(shí)例轉(zhuǎn)換而來(lái)。
- resourcepropertysource:繼承自propertiespropertysource,source指定為通過(guò)resource實(shí)例轉(zhuǎn)化為properties再轉(zhuǎn)換為map實(shí)例。
- stubpropertysource:propertysource的一個(gè)內(nèi)部類,source設(shè)置為null,實(shí)際上就是空實(shí)現(xiàn)。
- comparisonpropertysource:繼承自comparisonpropertysource,所有屬性訪問(wèn)方法強(qiáng)制拋出異常,作用就是一個(gè)不可訪問(wèn)屬性的空實(shí)現(xiàn)。
abstractenvironment中的屬性定義:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public static final string ignore_getenv_property_name = "spring.getenv.ignore";public static final string active_profiles_property_name = "spring.profiles.active";public static final string default_profiles_property_name = "spring.profiles.default";protected static final string reserved_default_profile_name = "default";private final set<string> activeprofiles = new linkedhashset<>();private final set<string> defaultprofiles = new linkedhashset<>(getreserveddefaultprofiles());private final mutablepropertysources propertysources = new mutablepropertysources(this.logger);private final configurablepropertyresolver propertyresolver = new propertysourcespropertyresolver(this.propertysources); |
上面的propertysources(mutablepropertysources類型)屬性就是用來(lái)存放propertysource列表的,propertysourcespropertyresolver是configurablepropertyresolver的實(shí)現(xiàn),默認(rèn)的profile就是字符串default。
mutablepropertysources的內(nèi)部屬性如下:
|
1
|
private final list<propertysource<?>> propertysourcelist = new copyonwritearraylist<>(); |
沒(méi)錯(cuò),這個(gè)就是最底層的存儲(chǔ)容器,也就是環(huán)境屬性都是存放在一個(gè)copyonwritearraylist<propertysource<?>>實(shí)例中。
mutablepropertysources是propertysources的子類,它提供了get(string name)、addfirst、addlast、addbefore、addafter、remove、replace等便捷方法,方便操作propertysourcelist集合的元素,這里挑選addbefore的源碼分析:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
public void addbefore(string relativepropertysourcename, propertysource<?> propertysource) { if (logger.isdebugenabled()) { logger.debug("adding propertysource '" + propertysource.getname() + "' with search precedence immediately higher than '" + relativepropertysourcename + "'"); } //前一個(gè)propertysource的name指定為relativepropertysourcename時(shí)候必須和添加的propertysource的name屬性不相同 assertlegalrelativeaddition(relativepropertysourcename, propertysource); //嘗試移除同名的propertysource removeifpresent(propertysource); //獲取前一個(gè)propertysource在copyonwritearraylist中的索引 int index = assertpresentandgetindex(relativepropertysourcename); //添加當(dāng)前傳入的propertysource到指定前一個(gè)propertysource的索引,相當(dāng)于relativepropertysourcename對(duì)應(yīng)的propertysource后移到原來(lái)索引值+1的位置 addatindex(index, propertysource);}protected void assertlegalrelativeaddition(string relativepropertysourcename, propertysource<?> propertysource) { string newpropertysourcename = propertysource.getname(); if (relativepropertysourcename.equals(newpropertysourcename)) { throw new illegalargumentexception( "propertysource named '" + newpropertysourcename + "' cannot be added relative to itself"); }}protected void removeifpresent(propertysource<?> propertysource) { this.propertysourcelist.remove(propertysource);}private int assertpresentandgetindex(string name) { int index = this.propertysourcelist.indexof(propertysource.named(name)); if (index == -1) { throw new illegalargumentexception("propertysource named '" + name + "' does not exist"); } return index;}private void addatindex(int index, propertysource<?> propertysource) { //注意,這里會(huì)再次嘗試移除同名的propertysource removeifpresent(propertysource); this.propertysourcelist.add(index, propertysource);} |
大多數(shù)propertysource子類的修飾符都是public,可以直接使用,這里寫(xiě)個(gè)小demo:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
mutablepropertysources mutablepropertysources = new mutablepropertysources();map<string, object> map = new hashmap<>(8);map.put("name", "throwable");map.put("age", 25);mappropertysource mappropertysource = new mappropertysource("map", map);mutablepropertysources.addlast(mappropertysource);properties properties = new properties();propertiespropertysource propertiespropertysource = new propertiespropertysource("prop", properties);properties.put("name", "doge");properties.put("gourp", "group-a");mutablepropertysources.addbefore("map", propertiespropertysource);system.out.println(mutablepropertysources); |
environment加載過(guò)程源碼分析
environment加載的源碼位于springapplication#prepareenvironment:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
private configurableenvironment prepareenvironment(springapplicationrunlisteners listeners,applicationarguments applicationarguments) {// create and configure the environment//創(chuàng)建configurableenvironment實(shí)例configurableenvironment environment = getorcreateenvironment();//啟動(dòng)參數(shù)綁定到configurableenvironment中configureenvironment(environment, applicationarguments.getsourceargs());//發(fā)布configurableenvironment準(zhǔn)備完畢事件listeners.environmentprepared(environment);//綁定configurableenvironment到當(dāng)前的springapplication實(shí)例中bindtospringapplication(environment);//這一步是非springmvc項(xiàng)目的處理,暫時(shí)忽略if (this.webapplicationtype == webapplicationtype.none) {environment = new environmentconverter(getclassloader()) .converttostandardenvironmentifnecessary(environment);}//綁定configurationpropertysourcespropertysource到configurableenvironment中,name為configurationproperties,實(shí)例是springconfigurationpropertysources,屬性實(shí)際是configurableenvironment中的mutablepropertysourcesconfigurationpropertysources.attach(environment);return environment;} |
這里重點(diǎn)看下getorcreateenvironment方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
private configurableenvironment getorcreateenvironment() { if (this.environment != null) { return this.environment; } //在springmvc項(xiàng)目,configurableenvironment接口的實(shí)例就是新建的standardservletenvironment實(shí)例 if (this.webapplicationtype == webapplicationtype.servlet) { return new standardservletenvironment(); } return new standardenvironment();}//reactive_web_environment_class=org.springframework.web.reactive.dispatcherhandler//mvc_web_environment_class=org.springframework.web.servlet.dispatcherservlet//mvc_web_environment_class={"javax.servlet.servlet","org.springframework.web.context.configurablewebapplicationcontext"}//這里,默認(rèn)就是webapplicationtype.servletprivate webapplicationtype deducewebapplicationtype() { if (classutils.ispresent(reactive_web_environment_class, null) && !classutils.ispresent(mvc_web_environment_class, null)) { return webapplicationtype.reactive; } for (string classname : web_environment_classes) { if (!classutils.ispresent(classname, null)) { return webapplicationtype.none; } } return webapplicationtype.servlet;} |
還有一個(gè)地方要重點(diǎn)關(guān)注:發(fā)布configurableenvironment準(zhǔn)備完畢事件listeners.environmentprepared(environment),實(shí)際上這里用到了同步的eventbus,事件的監(jiān)聽(tīng)者是configfileapplicationlistener,具體處理邏輯是onapplicationenvironmentpreparedevent方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
private void onapplicationenvironmentpreparedevent( applicationenvironmentpreparedevent event) { list<environmentpostprocessor> postprocessors = loadpostprocessors(); postprocessors.add(this); annotationawareordercomparator.sort(postprocessors); //遍歷所有的environmentpostprocessor對(duì)environment實(shí)例進(jìn)行處理 for (environmentpostprocessor postprocessor : postprocessors) { postprocessor.postprocessenvironment(event.getenvironment(), event.getspringapplication()); }}//從spring.factories文件中加載,一共有四個(gè)實(shí)例//configfileapplicationlistener//cloudfoundryvcapenvironmentpostprocessor//springapplicationjsonenvironmentpostprocessor//systemenvironmentpropertysourceenvironmentpostprocessorlist<environmentpostprocessor> loadpostprocessors() { return springfactoriesloader.loadfactories(environmentpostprocessor.class, getclass().getclassloader());} |
實(shí)際上,處理工作大部分都在configfileapplicationlistener中,見(jiàn)它的postprocessenvironment方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public void postprocessenvironment(configurableenvironment environment, springapplication application) { addpropertysources(environment, application.getresourceloader());}protected void addpropertysources(configurableenvironment environment, resourceloader resourceloader) { randomvaluepropertysource.addtoenvironment(environment); new loader(environment, resourceloader).load();} |
主要的配置環(huán)境加載邏輯在內(nèi)部類loader,loader會(huì)匹配多個(gè)路徑下的文件把屬性加載到configurableenvironment中,加載器主要是propertysourceloader的實(shí)例,例如我們用到application-${profile}.yaml文件做應(yīng)用主配置文件,使用的是yamlpropertysourceloader,這個(gè)時(shí)候activeprofiles也會(huì)被設(shè)置到configurableenvironment中。加載完畢之后,configurableenvironment中基本包含了所有需要加載的屬性(activeprofiles是這個(gè)時(shí)候被寫(xiě)入configurableenvironment)。值得注意的是,幾乎所有屬性都是key-value形式存儲(chǔ),如xxx.yyyy.zzzzz=value、xxx.yyyy[0].zzzzz=value-1、xxx.yyyy[1].zzzzz=value-2。loader中的邏輯相對(duì)復(fù)雜,有比較多的遍歷和過(guò)濾條件,這里不做展開(kāi)。
environment屬性訪問(wèn)源碼分析
上文提到過(guò),都是委托到propertysourcespropertyresolver,先看它的構(gòu)造函數(shù):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@nullableprivate final propertysources propertysources;public propertysourcespropertyresolver(@nullable propertysources propertysources) { this.propertysources = propertysources; } |
只依賴于一個(gè)propertysources實(shí)例,在springboot的springmvc項(xiàng)目中就是mutablepropertysources的實(shí)例。重點(diǎn)分析一下最復(fù)雜的一個(gè)方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
protected <t> t getproperty(string key, class<t> targetvaluetype, boolean resolvenestedplaceholders) { if (this.propertysources != null) { //遍歷所有的propertysource for (propertysource<?> propertysource : this.propertysources) { if (logger.istraceenabled()) { logger.trace("searching for key '" + key + "' in propertysource '" + propertysource.getname() + "'"); } object value = propertysource.getproperty(key); //選用第一個(gè)不為null的匹配key的屬性值 if (value != null) { if (resolvenestedplaceholders && value instanceof string) { //處理屬性占位符,如${server.port},底層委托到propertyplaceholderhelper完成 value = resolvenestedplaceholders((string) value); } logkeyfound(key, propertysource, value); //如果需要的話,進(jìn)行一次類型轉(zhuǎn)換,底層委托到defaultconversionservice完成 return convertvalueifnecessary(value, targetvaluetype); } } } if (logger.isdebugenabled()) { logger.debug("could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source"); } return null;} |
這里的源碼告訴我們,如果出現(xiàn)多個(gè)propertysource中存在同名的key,返回的是第一個(gè)propertysource對(duì)應(yīng)key的屬性值的處理結(jié)果,因此我們?nèi)绻枰远x一些環(huán)境屬性,需要十分清楚各個(gè)propertysource的順序。
擴(kuò)展-實(shí)現(xiàn)分散配置
在不使用springcloud配置中心的情況下,一般的springboot項(xiàng)目的配置文件如下:
- src
- main
- resources
- application-prod.yaml
- application-dev.yaml
- application-test.yaml
隨著項(xiàng)目發(fā)展,配置項(xiàng)越來(lái)越多,導(dǎo)致了application-${profile}.yaml迅速膨脹,大的配置文件甚至超過(guò)一千行,為了簡(jiǎn)化和劃分不同功能的配置,可以考慮把配置文件拆分如下:
- src
- main
- resources
- profiles
- dev
- business.yaml
- mq.json
- datasource.properties
- prod
- business.yaml
- mq.json
- datasource.properties
- test
- business.yaml
- mq.json
- datasource.properties
- application-prod.yaml
- application-dev.yaml
- application-test.yaml
外層的application-${profile}.yaml只留下項(xiàng)目的核心配置如server.port等,其他配置打散放在/profiles/${profile}/各自的配置文件中。實(shí)現(xiàn)方式是:依據(jù)當(dāng)前配置的spring.profiles.active屬性,讀取類路徑中指定文件夾下的配置文件中,加載到environment中,需要注意這一個(gè)加載步驟必須在spring刷新上下文方法最后一步finishrefresh之前完成(這一點(diǎn)原因可以參考之前在寫(xiě)過(guò)的springboot刷新上下文源碼的分析),否則有可能會(huì)影響到占位符屬性的自動(dòng)裝配(例如使用了@value("${filed}"))。
先定義一個(gè)屬性探索者接口:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public interface propertysourcedetector { /** * 獲取支持的文件后綴數(shù)組 * * @return string[] */ string[] getfileextensions(); /** * 加載目標(biāo)文件屬性到環(huán)境中 * * @param environment environment * @param name name * @param resource resource * @throws ioexception ioexception */ void load(configurableenvironment environment, string name, resource resource) throws ioexception;} |
然后需要一個(gè)抽象屬性探索者把resource轉(zhuǎn)換為字符串,額外提供map的縮進(jìn)、添加propertysource到environment等方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
public abstract class abstractpropertysourcedetector implements propertysourcedetector { private static final string servlet_environment_class = "org.springframework.web." + "context.support.standardservletenvironment"; public boolean support(string fileextension) { string[] fileextensions = getfileextensions(); return null != fileextensions && arrays.stream(fileextensions).anymatch(extension -> extension.equals(fileextension)); } private string findpropertysource(mutablepropertysources sources) { if (classutils.ispresent(servlet_environment_class, null) && sources .contains(standardservletenvironment.jndi_property_source_name)) { return standardservletenvironment.jndi_property_source_name; } return standardenvironment.system_properties_property_source_name; } protected void addpropertysource(configurableenvironment environment, propertysource<?> source) { mutablepropertysources sources = environment.getpropertysources(); string name = findpropertysource(sources); if (sources.contains(name)) { sources.addbefore(name, source); } else { sources.addfirst(source); } } protected map<string, object> flatten(map<string, object> map) { map<string, object> result = new linkedhashmap<>(); flatten(null, result, map); return result; } private void flatten(string prefix, map<string, object> result, map<string, object> map) { string nameprefix = (prefix != null ? prefix + "." : ""); map.foreach((key, value) -> extract(nameprefix + key, result, value)); } @suppresswarnings("unchecked") private void extract(string name, map<string, object> result, object value) { if (value instanceof map) { flatten(name, result, (map<string, object>) value); } else if (value instanceof collection) { int index = 0; for (object object : (collection<object>) value) { extract(name + "[" + index + "]", result, object); index++; } } else { result.put(name, value); } } protected string getcontentstringfromresource(resource resource) throws ioexception { return streamutils.copytostring(resource.getinputstream(), charset.forname("utf-8")); }} |
上面的方法參考springapplicationjsonenvironmentpostprocessor,然后編寫(xiě)各種類型配置屬性探索者的實(shí)現(xiàn):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
//json@slf4jpublic class jsonpropertysourcedetector extends abstractpropertysourcedetector { private static final jsonparser json_parser = jsonparserfactory.getjsonparser(); @override public string[] getfileextensions() { return new string[]{"json"}; } @override public void load(configurableenvironment environment, string name, resource resource) throws ioexception { try { map<string, object> map = json_parser.parsemap(getcontentstringfromresource(resource)); map<string, object> target = flatten(map); addpropertysource(environment, new mappropertysource(name, target)); } catch (exception e) { log.warn("加載json文件屬性到環(huán)境變量失敗,name = {},resource = {}", name, resource); } }}//propertiespublic class propertiespropertysourcedetector extends abstractpropertysourcedetector { @override public string[] getfileextensions() { return new string[]{"properties", "conf"}; } @suppresswarnings("unchecked") @override public void load(configurableenvironment environment, string name, resource resource) throws ioexception { map map = propertiesloaderutils.loadproperties(resource); addpropertysource(environment, new mappropertysource(name, map)); }}//yaml@slf4jpublic class yamlpropertysourcedetector extends abstractpropertysourcedetector { private static final jsonparser yaml_parser = new yamljsonparser(); @override public string[] getfileextensions() { return new string[]{"yaml", "yml"}; } @override public void load(configurableenvironment environment, string name, resource resource) throws ioexception { try { map<string, object> map = yaml_parser.parsemap(getcontentstringfromresource(resource)); map<string, object> target = flatten(map); addpropertysource(environment, new mappropertysource(name, target)); } catch (exception e) { log.warn("加載yaml文件屬性到環(huán)境變量失敗,name = {},resource = {}", name, resource); } }} |
子類的全部propertysource都是mappropertysource,name為文件的名稱,所有propertysource都用addbefore方法插入到systemproperties的前面,主要是為了提高匹配屬性的優(yōu)先級(jí)。接著需要定義一個(gè)屬性探索者的合成類用來(lái)裝載所有的子類:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
public class propertysourcedetectorcomposite implements propertysourcedetector { private static final string default_suffix = "properties"; private final list<abstractpropertysourcedetector> propertysourcedetectors = new arraylist<>(); public void addpropertysourcedetector(abstractpropertysourcedetector sourcedetector) { propertysourcedetectors.add(sourcedetector); } public void addpropertysourcedetectors(list<abstractpropertysourcedetector> sourcedetectors) { propertysourcedetectors.addall(sourcedetectors); } public list<abstractpropertysourcedetector> getpropertysourcedetectors() { return collections.unmodifiablelist(propertysourcedetectors); } @override public string[] getfileextensions() { list<string> fileextensions = new arraylist<>(8); for (abstractpropertysourcedetector propertysourcedetector : propertysourcedetectors) { fileextensions.addall(arrays.aslist(propertysourcedetector.getfileextensions())); } return fileextensions.toarray(new string[0]); } @override public void load(configurableenvironment environment, string name, resource resource) throws ioexception { if (resource.isfile()) { string filename = resource.getfile().getname(); int index = filename.lastindexof("."); string suffix; if (-1 == index) { //如果文件沒(méi)有后綴,當(dāng)作properties處理 suffix = default_suffix; } else { suffix = filename.substring(index + 1); } for (abstractpropertysourcedetector propertysourcedetector : propertysourcedetectors) { if (propertysourcedetector.support(suffix)) { propertysourcedetector.load(environment, name, resource); return; } } } }} |
最后添加一個(gè)配置類作為入口:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public class propertysourcedetectorconfiguration implements importbeandefinitionregistrar { private static final string path_prefix = "profiles"; @override public void registerbeandefinitions(annotationmetadata importingclassmetadata, beandefinitionregistry registry) { defaultlistablebeanfactory beanfactory = (defaultlistablebeanfactory) registry; configurableenvironment environment = beanfactory.getbean(configurableenvironment.class); list<abstractpropertysourcedetector> propertysourcedetectors = new arraylist<>(); configurepropertysourcedetectors(propertysourcedetectors, beanfactory); propertysourcedetectorcomposite propertysourcedetectorcomposite = new propertysourcedetectorcomposite(); propertysourcedetectorcomposite.addpropertysourcedetectors(propertysourcedetectors); string[] activeprofiles = environment.getactiveprofiles(); resourcepatternresolver resourcepatternresolver = new pathmatchingresourcepatternresolver(); try { for (string profile : activeprofiles) { string location = path_prefix + file.separator + profile + file.separator + "*"; resource[] resources = resourcepatternresolver.getresources(location); for (resource resource : resources) { propertysourcedetectorcomposite.load(environment, resource.getfilename(), resource); } } } catch (ioexception e) { throw new illegalstateexception(e); } } private void configurepropertysourcedetectors(list<abstractpropertysourcedetector> propertysourcedetectors, defaultlistablebeanfactory beanfactory) { map<string, abstractpropertysourcedetector> beansoftype = beanfactory.getbeansoftype(abstractpropertysourcedetector.class); for (map.entry<string, abstractpropertysourcedetector> entry : beansoftype.entryset()) { propertysourcedetectors.add(entry.getvalue()); } propertysourcedetectors.add(new jsonpropertysourcedetector()); propertysourcedetectors.add(new yamlpropertysourcedetector()); propertysourcedetectors.add(new propertiespropertysourcedetector()); }} |
準(zhǔn)備就緒,在/resources/profiles/dev下面添加兩個(gè)文件app.json和conf:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
//app.json{ "app": { "name": "throwable", "age": 25 }}//confname=doge |
項(xiàng)目的application.yaml添加屬性spring.profiles.active: dev,最后添加一個(gè)commandlinerunner的實(shí)現(xiàn)用來(lái)觀察數(shù)據(jù):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
@slf4j@componentpublic class customcommandlinerunner implements commandlinerunner { @value("${app.name}") string name; @value("${app.age}") integer age; @autowired configurableenvironment configurableenvironment; @override public void run(string... args) throws exception { log.info("name = {},age = {}", name, age); }} |

自動(dòng)裝配的屬性值和environment實(shí)例中的屬性和預(yù)期一樣,改造是成功的。
小結(jié)
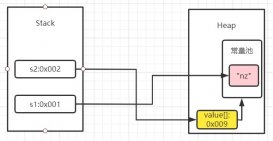
spring中的環(huán)境屬性管理的源碼個(gè)人認(rèn)為是最清晰和簡(jiǎn)單的:從文件中讀取數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)化為key-value結(jié)構(gòu),key-value結(jié)構(gòu)存放在一個(gè)propertysource實(shí)例中,然后得到的多個(gè)propertysource實(shí)例存放在一個(gè)copyonwritearraylist中,屬性訪問(wèn)的時(shí)候總是遍歷copyonwritearraylist中的propertysource進(jìn)行匹配。可能相對(duì)復(fù)雜的就是占位符的解析和參數(shù)類型的轉(zhuǎn)換,后者牽連到converter體系,這些不在本文的討論范圍內(nèi)。最后附上一張environment存儲(chǔ)容器的示例圖:

參考資料:
spring-boot-starter-web:2.0.3.release源碼。
總結(jié)
以上就是這篇文章的全部?jī)?nèi)容了,希望本文的內(nèi)容對(duì)大家的學(xué)習(xí)或者工作具有一定的參考學(xué)習(xí)價(jià)值,如果有疑問(wèn)大家可以留言交流,謝謝大家對(duì)服務(wù)器之家的支持。
原文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/throwable/p/9411100.html