1 系統(tǒng)吞吐量的簡單介紹
一個系統(tǒng)的吞度量(承壓能力)與request對CPU的消耗、外部接口、IO等等緊密關(guān)聯(lián)。
單個reqeust 對CPU消耗越高,外部系統(tǒng)接口、IO影響速度越慢,系統(tǒng)吞吐能力越低,反之越高。
系統(tǒng)吞吐量幾個重要參數(shù):TPS、并發(fā)數(shù)、響應時間
- TPS:每秒鐘處理的事務數(shù)量
- 并發(fā)量: 系統(tǒng)同時處理請求數(shù)(事務數(shù))
- 響應時間: 一般取平均響應時間
TPS= 并發(fā)量/平均響應時間
這里因為說的事務如果是單一接口請求,我們也可以認為TPS即為QPS。
下面舉例說明:
比如3000個用戶(并發(fā)量)同時訪問待測試接口,在用戶端統(tǒng)計,3000個用戶平均得到響應的時間為1188.538ms。所以TPS=3000/1.188538s= 2524.11 q/s。
我們就可以這樣描述本次測試,在3000個并發(fā)量的情況下,TPS為2524.11,平均響應事件為1188.538ms
Tps:在實際測試中表現(xiàn)為:
一個系統(tǒng)吞吐量通常由TPS、并發(fā)數(shù)兩個因素決定,每套系統(tǒng)這兩個值都有一個相對極限值,在應用場景訪問壓力下,只要某一項達 到系統(tǒng)最高值,系統(tǒng)的吞吐量就上不去了,如果壓力繼續(xù)增大,系統(tǒng)的吞吐量反而會下降,原因是系統(tǒng)超負荷工作,上下文切換、內(nèi)存等等其它消耗導致系統(tǒng)性能下降。
實際表現(xiàn)為tps即先上升后下降,我們需要找到性能拐點。并得到限制瓶頸。
2 測試方法
參考文獻(詳細輸出說明):
http://m.ythuaji.com.cn/article/220606.html
2.1 客戶端測試工具
我們采用apacheBench 工具進行測試。
ubuntu安裝ab:
|
1
|
sudo apt-get install apache2-utils |
linux默認登錄端口只能打開1024個文件,因為在linux一切皆文件,所以ab并發(fā)數(shù)受到整個打開文件數(shù)的限制,需要使用ulimit -n 10000(打開文件數(shù))進行修改后才能支持較大的并發(fā)。本人測試修改到15000。
2.1.1 GET方法
ab -n 100 -c 100 https://www.baidu.com/index.html
-n:請求 總數(shù)
-c:并發(fā)用戶數(shù).
-url:待測api。
當測試發(fā)起請求數(shù)量較少,完成較快,無中間過程顯示。在請求數(shù)量很多時會分行顯示當前完成數(shù)量。
2.1.2 POST方法
|
1
|
ab -n 10 -c 1 -T 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' -H "Authorization:Bearer 2393d8db9b9d7f4b9d1570cc8776bca69b421b62" -p ./post http://172.28.28.17:3017/oauth2/token |
- -H:可以設(shè)置響應header
- -T: Post http header類型 默認為text/plain
- -P:Post body內(nèi)容, ab要求寫在文件中,-p后跟文件目錄,文件內(nèi)容如name=hello&password=1234
2.1.3 測試結(jié)果解讀
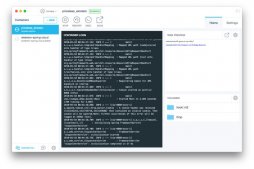
來份ab的測試輸出:

ab -n 10 -c 2 上圖結(jié)果為總請求10 并發(fā)為2的結(jié)果
我們主要關(guān)注的輸出信息為:
- Concurrency Level: 10 //并發(fā)級別,也就是并發(fā)數(shù),請求中-c參數(shù)指定的數(shù)量
- Time taken for tests: 1.093 seconds //本次測試總共花費的時間
- Complete requests: 100 //本次測試總共發(fā)起的請求數(shù)量
- Failed requests: 0 //失敗的請求數(shù)量。因網(wǎng)絡(luò)原因或服務器性能原因,發(fā)起的請求并不一定全部成功,通過該數(shù)值和Complete requests相除可以計算請求的失敗率,作為測試結(jié)果的重要參考。
- Total transferred: 103314 bytes //總共傳輸?shù)臄?shù)據(jù)量,指的是ab從被測服務器接收到的總數(shù)據(jù)量,包括index.html的文本內(nèi)容和請求頭信息。
- Requests per second: 91.50 [#/sec] (mean) //平均(mean)每秒完成的請求數(shù):QPS,這是一個平均值,等于Complete requests/Time taken for tests=100/1.093=91.50
- Time per request: 109.287 [ms] (mean) //從用戶角度看,完成一個請求所需要的時間(因用戶數(shù)量不止一個,服務器完成10個請求,平均每個用戶才接收到一個完整的返回,所以該值是下一項數(shù)值的10倍。)
- Time per request: 10.929 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)// 服務器完成一個請求的時間。
- Transfer rate: 92.32 [Kbytes/sec] received //網(wǎng)絡(luò)傳輸速度。對于大文件的請求測試,這個值很容易成為系統(tǒng)瓶頸所在。要確定該值是不是瓶頸,需要了解客戶端和被測服務器之間的網(wǎng)絡(luò)情況,包括網(wǎng)絡(luò)帶寬和網(wǎng)卡速度等信息。
其中我們最為關(guān)注的為Requests per second: 即tps。我們將它最為服務器性能最為重要的指標。
2.2服務器端檢測方法
可以通過 iftop命令和nethogs -d 對服務器網(wǎng)絡(luò)情況進行檢測。
可以通過iptables命令監(jiān)控服務器端口流量。
可以通過 top | grep “node” 對內(nèi)存和cpu進行判斷。
對云上測試 可以使用云主機后臺,但后臺參數(shù)是分鐘級后的平均值。
感覺好像這樣測優(yōu)點蠢
3 實際測試
使用apacheBench 可以使用編寫shell腳本進行多次測試。可以將待測api 放入api數(shù)組并修改循環(huán)數(shù)量,實現(xiàn)一次測試多個api并生成關(guān)鍵參數(shù)xls文件。現(xiàn)在看來還是原來太天真才會有這種想法。
3.1 shell腳本
使用說明:a 是請求總數(shù) ,b是并發(fā)用戶數(shù)一一對應,即a[0]對應b[0],傳入?yún)?shù)第一個是待測api服務器地址,第二個是api所需參數(shù)。api設(shè)置在api數(shù)組中。添加多個api 或同意api多組測試請修改循環(huán)計數(shù)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
echo "you maybe use this sh like:"$0" serverIP userParam"a=(1000 2000 4000 6000 7000)#待測請求總數(shù)b=(50 100 200 300 400)#并發(fā)用戶數(shù)runTime=$(date +%Y%m%d%H%M%S)if [ -z "$1"]then serverip="http://127.0.0.1"else serverip=$1fiif [ -z "$2"]then param="deviceid=XXX&bindingplatform=XXX&bindingid=XXX"else param=$2fifilename=${runTime}"-test.log"touch filename#api=('XXX'${param} 'XXX'${param} '/users/account')api=('XXX'${param})echo "********webserver test info*************"echo "testTime :"$(date) echo "LogName :"${filename}echo "serverIP :"${serverip}echo "userparam:"${param}echo "********webserver test info*************"#echo ${filename}for j in {0..0}#待測api個數(shù) 即api數(shù)組數(shù)do echo "API test:"${serverip}${api[j]} for i in {0..4}#待測api測試次數(shù) 5次也就是對應a b數(shù)組有個五個值 do ab -r -k -n ${a[i]} -c ${b[i]} -C ${param} ${serverip}${api[j]} | grep -e"Document Path:" -e "Complete requests:" -e "Concurrency Level:" -e"Failed requests:" -e"Time taken for tests:" -e "Requests per second:" -e "Time per request" -e"Total transferred: " >> ${filename} donedonesed -i 's/^.\{24\}//g' ${filename}# 按照時間生成txt文件 并按上面的參數(shù)進行提取。export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./change ${filename} ${runTime}"report.xls"#chang 函數(shù)功能是將txt中關(guān)鍵數(shù)據(jù)變成xls文件。rm ${filename} |
3.2 C++提取程序:使用了libxl.h
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
|
#include <iostream>#include <fstream>#include <string>#include "libxl.h"using namespace std;using namespace libxl;int main(int agrc, char *argc[]){ //cout << "helloworld" << endl; fstream f; ifstream ifile(argc[1]); string temp; int i = 0, j=1, k = 0; Book* book = xlCreateBook();//創(chuàng)建一個二進制格式的XLS(Execl97-03)的實例,在使用前必須先調(diào)用這個函數(shù)創(chuàng)建操作excel的對象 //book->setKey(......);//如果購買了該庫,則設(shè)置相應的key,若沒有購買,則不用這行 if (book)//是否創(chuàng)建實例成功 { Sheet* sheet = book->addSheet("Sheet1");//添加一個工作表 for(i=0;i<30;i++) { for(j=0;j<10;j++){ sheet->setCol(i, j, 20);//設(shè)置列寬,格式等 } } i=0; j=1; if (sheet) { sheet->writeStr(j, 0, "API"); sheet->writeStr(j, 1, "Concurrency Level"); sheet->writeStr(j, 2, "Time taken for tests"); sheet->writeStr(j, 3, "Complete requests"); sheet->writeStr(j, 4, "Failed requests"); sheet->writeStr(j, 5, "Total transferred"); sheet->writeStr(j, 6, "Requests per second"); sheet->writeStr(j, 7, "Time per reques(user)"); sheet->writeStr(j, 8, "Time per reques(server)"); j++; while (getline(ifile, temp)) { if (temp[0] == '/'){ f << temp << " "; sheet->writeStr(j, i, temp.c_str()); } else if (temp.find('[') != string::npos){ f << temp.substr(0, temp.find('[') - 1) << " "; sheet->writeStr(j, i, temp.substr(0, temp.find('[') - 1).c_str()); } else if (temp.find('b') != string::npos){ f << temp.substr(0, temp.find('b') - 1) << " "; sheet->writeStr(j, i, temp.substr(0, temp.find('b') - 1).c_str()); } else if (temp.find('s') != string::npos){ sheet->writeStr(j, i, temp.substr(0, temp.find('s') - 1).c_str()); f << temp.substr(0, temp.find('s') - 1) << " "; } else{ sheet->writeStr(j, i, temp.c_str()); f << temp << " "; } i++; if (i == 9){ f << " " << endl; i = 0; j++; } } ifile.close(); } if (book->save(argc[2]))//保存到example.xls { //..... } else { std::cout << book->errorMessage() << std::endl; } book->release();} return 0;} |
4 測試中遇到一些問題
在用云主機時要注意一下云主機帶寬的問題,小水管很可能成為瓶頸。
ab軟件中Total transferred 與端口流量有差距。端口流量大于Total transferred,猜測是有封包的因素。所以不能把Total transferred作為服務器消耗的流量來處理,用于計算云上某些按流量消耗的服務。
git:https://github.com/CollapsarLi/server_apachebench_shell.git
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務器之家。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37263637/article/details/78558890