本文實例講述了MySQL聯合索引功能與用法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
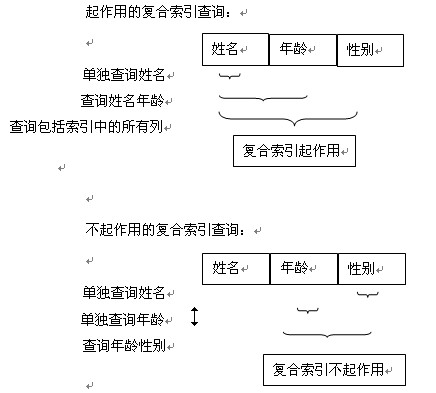
聯合索引又叫復合索引。對于復合索引:Mysql從左到右的使用索引中的字段,一個查詢可以只使用索引中的一部份,但只能是最左側部分。例如索引是key index (a,b,c). 可以支持a | a,b| a,b,c 3種組合進行查找,但不支持 b,c進行查找 .當最左側字段是常量引用時,索引就十分有效。
兩個或更多個列上的索引被稱作復合索引。
利用索引中的附加列,您可以縮小搜索的范圍,但使用一個具有兩列的索引 不同于使用兩個單獨的索引。復合索引的結構與電話簿類似,人名由姓和名構成,電話簿首先按姓氏對進行排序,然后按名字對有相同姓氏的人進行排序。如果您知 道姓,電話簿將非常有用;如果您知道姓和名,電話簿則更為有用,但如果您只知道名不姓,電話簿將沒有用處。
所以說創建復合索引時,應該仔細考慮列的順序。對索引中的所有列執行搜索或僅對前幾列執行搜索時,復合索引非常有用;僅對后面的任意列執行搜索時,復合索引則沒有用處。
如:建立 姓名、年齡、性別的復合索引。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
create table test(a int,b int,c int,KEY a(a,b,c)); 優: select * from test where a=10 and b>50差: select * from test where a>50優: select * from test order by a差: select * from test order by b差: select * from test order by c優: select * from test where a=10 order by a優: select * from test where a=10 order by b差: select * from test where a=10 order by c優: select * from test where a>10 order by a差: select * from test where a>10 order by b差: select * from test where a>10 order by c優: select * from test where a=10 and b=10 order by a優: select * from test where a=10 and b=10 order by b優: select * from test where a=10 and b=10 order by c優: select * from test where a=10 and b=10 order by a優: select * from test where a=10 and b>10 order by b差: select * from test where a=10 and b>10 order by c |
索引原則
1.索引越少越好
原因:主要在修改數據時,第個索引都要進行更新,降低寫速度。
2.最窄的字段放在鍵的左邊
3.避免file sort排序,臨時表和表掃描.
希望本文所述對大家MySQL數據庫計有所幫助。
原文鏈接:http://blog.csdn.net/u013474436/article/details/48373043