spring 基于注解啟動
主要有兩個class實現注解啟動
- annotationconfigapplicationcontext
- annotationconfigwebapplicationcontext
我們以annotationconfigapplicationcontext 為研究對象

annotationconfigapplicationcontext.png
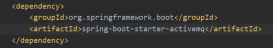
引入spring 最小依賴
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency> <groupid>org.springframework</groupid> <artifactid>spring-context</artifactid> <version>${spring.version}</version></dependency> |
編寫器啟動代碼
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public static void main(string[] args) {annotationconfigapplicationcontext applicationcontext = new annotationconfigapplicationcontext();applicationcontext.register(beanconfig.class);applicationcontext.refresh();date date = applicationcontext.getbean("date",date.class);system.out.println(date);} |
annotationconfigapplicationcontext 構造函數
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public annotationconfigapplicationcontext() { //負責注冊class ,讀取器 this.reader = new annotatedbeandefinitionreader(this); //負責掃描指定類路徑下的class,注冊bean this.scanner = new classpathbeandefinitionscanner(this);} |
annotatedbeandefinitionreader 構造方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public annotatedbeandefinitionreader(beandefinitionregistry registry) { this(registry, getorcreateenvironment(registry));}public annotatedbeandefinitionreader(beandefinitionregistry registry, environment environment) { assert.notnull(registry, "beandefinitionregistry must not be null"); assert.notnull(environment, "environment must not be null"); this.registry = registry; //初始化conditionevaluator this.conditionevaluator = new conditionevaluator(registry, environment, null); /** 在給定的注冊表中註冊所有相關的post processors * 判斷容器是否已經存在給定注冊表的bean,如果沒有注冊bean,并將bean放入容器中 * 把所有的處理處理器列出來 * configurationclasspostprocessor 內部管理的配置注解處理器 * autowiredannotationbeanpostprocessor 內部管理@autowired 的處理器 * requiredannotationbeanpostprocessor @required的處理器 * commonannotationbeanpostprocessor jsr-250注解處理器 ,先判斷是否支持jsr,如果支持注冊 * persistenceannotationbeanpostprocessor jpa管理 先使用類加載器查找是否存在,如果有這個包則注冊 * eventlistenermethodprocessor @eventlistener的處理器 * defaulteventlistenerfactory 管理eventlistenerfactory處理器 */ annotationconfigutils.registerannotationconfigprocessors(this.registry);} |
conditionevaluator 這個對象干什么,點擊進去
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public conditionevaluator(@nullable beandefinitionregistry registry, @nullable environment environment, @nullable resourceloader resourceloader) { this.context = new conditioncontextimpl(registry, environment, resourceloader); } //conditioncontextimpl 實現了conditioncontext接口,conditionevaluator靜態內部類 public conditioncontextimpl(@nullable beandefinitionregistry registry, @nullable environment environment, @nullable resourceloader resourceloader) { this.registry = registry; this.beanfactory = deducebeanfactory(registry); this.environment = (environment != null ? environment : deduceenvironment(registry)); this.resourceloader = (resourceloader != null ? resourceloader : deduceresourceloader(registry)); this.classloader = deduceclassloader(resourceloader, this.beanfactory); } |
可以知道conditionevaluator使用外部傳參的方法初始化了spring容器頂級對象
beanfactory,environment,resourceloader,classloader。在將這些傳給conditioncontextimpl為接下來的解析@conditional注解做好準備
classpathbeandefinitionscanner構造函數
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
public classpathbeandefinitionscanner(beandefinitionregistry registry) { this(registry, true);}public classpathbeandefinitionscanner(beandefinitionregistry registry, boolean usedefaultfilters) { this(registry, usedefaultfilters, getorcreateenvironment(registry));}public classpathbeandefinitionscanner(beandefinitionregistry registry, boolean usedefaultfilters, environment environment) { this(registry, usedefaultfilters, environment, (registry instanceof resourceloader ? (resourceloader) registry : null));}public classpathbeandefinitionscanner(beandefinitionregistry registry, boolean usedefaultfilters, environment environment, @nullable resourceloader resourceloader) { assert.notnull(registry, "beandefinitionregistry must not be null"); this.registry = registry; if (usedefaultfilters) { registerdefaultfilters(); } setenvironment(environment); setresourceloader(resourceloader);}protected void registerdefaultfilters() { this.includefilters.add(new annotationtypefilter(component.class)); classloader cl = classpathscanningcandidatecomponentprovider.class.getclassloader(); try { this.includefilters.add(new annotationtypefilter( ((class<? extends annotation>) classutils.forname("javax.annotation.managedbean", cl)), false)); logger.debug("jsr-250 'javax.annotation.managedbean' found and supported for component scanning"); } catch (classnotfoundexception ex) { } try { this.includefilters.add(new annotationtypefilter( ((class<? extends annotation>) classutils.forname("javax.inject.named", cl)), false)); logger.debug("jsr-330 'javax.inject.named' annotation found and supported for component scanning"); } catch (classnotfoundexception ex) { // jsr-330 api not available - simply skip. }} |
繞了地球幾圈了,其實就是將spring 頂級接口 environment,resourceloader賦值,使用默認注解過濾器,首先將@component加入list中,判斷當前環境是否支持jsr-250,jsr-330,相應加入過濾器中。也就是這個掃描器默認只掃描@component或者jsr-250,jsr-330的標記的class。
applicationcontext.register(beanconfig.class)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
public void register(class<?>... annotatedclasses) { assert.notempty(annotatedclasses, "at least one annotated class must be specified"); this.reader.register(annotatedclasses); //調用 剛剛初始化讀取器 } |============================annotatedbeandefinitionreader 讀取器代碼====================================================================================================== public void register(class<?>... annotatedclasses) { for (class<?> annotatedclass : annotatedclasses) { registerbean(annotatedclass); } } public void registerbean(class<?> annotatedclass) { doregisterbean(annotatedclass, null, null, null); } /** *從給定的bean解析class給定的注解,執行相應的初始化,保存到spring容器中 */ <t> void doregisterbean(class<t> annotatedclass, @nullable supplier<t> instancesupplier, @nullable string name, @nullable class<? extends annotation>[] qualifiers, beandefinitioncustomizer... definitioncustomizers) { //根據class的annotated 得出元數據 annotationmetadata annotatedgenericbeandefinition abd = new annotatedgenericbeandefinition(annotatedclass); /** * 判斷注冊的class 是否包含@conditional注解,如果有獲取全部value,放入list中 * 排序后,遍歷所有的conditiion的實現,使用反射獲取對象,執行matches方法, * 如果發現有返回false,中斷循環直接返回true, */ if (this.conditionevaluator.shouldskip(abd.getmetadata())) { //如果 @conditional條件不滿足,不進行注冊 return; } abd.setinstancesupplier(instancesupplier); //解析class是否有@scope,解析@scope注解返回scopemetadata對象,沒有直接返回空 scopemetadata scopemetadata = this.scopemetadataresolver.resolvescopemetadata(abd); abd.setscope(scopemetadata.getscopename()); //判斷注解上value是否有值,有就使用這個作為beanname,沒有則取類名 string beanname = (name != null ? name : this.beannamegenerator.generatebeanname(abd, this.registry)); //繼續解析annotationmetadata的@lazy,@primary,@dependson,@role,@description的注解,放入結果放入對象的屬性中 annotationconfigutils.processcommondefinitionannotations(abd); //這個類只是beandefinition 包裝類 beandefinitionholder definitionholder = new beandefinitionholder(abd, beanname); //是否需要代理類,如果是則修改內部屬性,重新生成beandefinition 對象 definitionholder = annotationconfigutils.applyscopedproxymode(scopemetadata, definitionholder, this.registry); //調用defaultlistablebeanfactory.registerbeandefinition的方法,做一些安全性校驗再,將definitionholder 放入register容器中 beandefinitionreaderutils.registerbeandefinition(definitionholder, this.registry); } |
這個方法就是將注冊的bean,解析class上的注解,初始化注解數據,做相應處理,轉化成beandefinition ,放入spring 容器中保存起來。
我們看下beandefinition是怎么實現注冊到spring的容器中,主要由defaultlistablebeanfactory.registerbeandefinition來實現
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
public void registerbeandefinition(string beanname, beandefinition beandefinition) throws beandefinitionstoreexception { assert.hastext(beanname, "bean name must not be empty"); assert.notnull(beandefinition, "beandefinition must not be null"); if (beandefinition instanceof abstractbeandefinition) { try { //對beandefinition 進行校驗判斷methodoverrides不能為空,必須擁有工廠方法 ((abstractbeandefinition) beandefinition).validate(); } catch (beandefinitionvalidationexception ex) { throw new beandefinitionstoreexception(beandefinition.getresourcedescription(), beanname, "validation of bean definition failed", ex); } } beandefinition oldbeandefinition; oldbeandefinition = this.beandefinitionmap.get(beanname); if (oldbeandefinition != null) { //這個方法是判斷是否允許出現重名bean,并且是不同的定義bean,是否可以覆蓋前者 if (!isallowbeandefinitionoverriding()) { throw new beandefinitionstoreexception(beandefinition.getresourcedescription(), beanname, "cannot register bean definition [" + beandefinition + "] for bean '" + beanname + "': there is already [" + oldbeandefinition + "] bound."); } else if (oldbeandefinition.getrole() < beandefinition.getrole()) { // e.g. was role_application, now overriding with role_support or role_infrastructure if (this.logger.iswarnenabled()) { this.logger.warn("overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanname + "' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" + oldbeandefinition + "] with [" + beandefinition + "]"); } } else if (!beandefinition.equals(oldbeandefinition)) { if (this.logger.isinfoenabled()) { this.logger.info("overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanname + "' with a different definition: replacing [" + oldbeandefinition + "] with [" + beandefinition + "]"); } } else { if (this.logger.isdebugenabled()) { this.logger.debug("overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanname + "' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + oldbeandefinition + "] with [" + beandefinition + "]"); } } this.beandefinitionmap.put(beanname, beandefinition); } else { //調用alreadycreated.isempty(),alreadycreated set對象,保存已經創建beanname //文檔中表示created,跟這里注冊應該不是同一個行為,這個要看到后面才知道什么意思 if (hasbeancreationstarted()) { synchronized (this.beandefinitionmap) {//更新數據 this.beandefinitionmap.put(beanname, beandefinition); list<string> updateddefinitions = new arraylist<>(this.beandefinitionnames.size() + 1); updateddefinitions.addall(this.beandefinitionnames); updateddefinitions.add(beanname); this.beandefinitionnames = updateddefinitions; if (this.manualsingletonnames.contains(beanname)) { set<string> updatedsingletons = new linkedhashset<>(this.manualsingletonnames); updatedsingletons.remove(beanname); this.manualsingletonnames = updatedsingletons; } } } else { //spring beandefinition 容器,一個map轉載 this.beandefinitionmap.put(beanname, beandefinition); //保存beanname,主要用于記錄每個bean注冊順序 this.beandefinitionnames.add(beanname); //刪除單例,注冊成一個普通bean this.manualsingletonnames.remove(beanname); } this.frozenbeandefinitionnames = null; } if (oldbeandefinition != null || containssingleton(beanname)) { //更新spring容器里beanname resetbeandefinition(beanname); } } |
將beandefinition注冊到spring容器中,并沒有太多復雜的邏輯,只是做一些安全性的檢查。
beandefinition
一個beandefinition描述了一個bean的實例,包括屬性值,構造方法參數值和繼承自它的類的更多信息。beandefinition僅僅是一個最簡單的接口,主要功能是允許beanfactorypostprocessor 例如propertyplaceholderconfigure 能夠檢索并修改屬性值和別的bean的元數據(譯注)
spring 容器beandefinition主要分為rootbeandefinition,annotatedgenericbeandefinition這兩種
- rootbeandefinition spring factory中的特定bean
- annotatedgenericbeandefinition 用戶自定義bean
spring 啟動流程總結

annotationconfigapplicationcontext 初始化.png
這些beandefinition只是放入到spirng 容器中,并沒有進行任何初始化對象的操作,真正的ioc操作都在refresh(),這個方法有空再進行分析。
總結
以上就是這篇文章的全部內容了,希望本文的內容對大家的學習或者工作具有一定的參考學習價值,如果有疑問大家可以留言交流,謝謝大家對服務器之家的支持。
原文鏈接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/573bdae020e9