最近項(xiàng)目需要用到spring security的權(quán)限控制,故花了點(diǎn)時(shí)間簡單的去看了一下其權(quán)限控制相關(guān)的源碼(版本為4.2)。
accessdecisionmanager
spring security是通過accessdecisionmanager進(jìn)行授權(quán)管理的,先來張官方圖鎮(zhèn)樓。

accessdecisionmanager
accessdecisionmanager 接口定義了如下方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
//調(diào)用accessdecisionvoter進(jìn)行投票(關(guān)鍵方法)void decide(authentication authentication, object object, collection<configattribute> configattributes) throws accessdeniedexception, insufficientauthenticationexception;boolean supports(configattribute attribute);boolean supports(class clazz); |
接下來看看它的實(shí)現(xiàn)類的具體實(shí)現(xiàn):
affirmativebased
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
public void decide(authentication authentication, object object, collection<configattribute> configattributes) throws accessdeniedexception { int deny = 0; for (accessdecisionvoter voter : getdecisionvoters()) { //調(diào)用accessdecisionvoter進(jìn)行vote(我們姑且稱之為投票吧),后面再看vote的源碼。 int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configattributes); if (logger.isdebugenabled()) { logger.debug("voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result); } switch (result) { case accessdecisionvoter.access_granted://值為1 //只要有voter投票為access_granted,則通過 return; case accessdecisionvoter.access_denied://值為-1 deny++; break; default: break; } } if (deny > 0) { //如果有兩個(gè)及以上accessdecisionvoter(姑且稱之為投票者吧)都投access_denied,則直接就不通過了 throw new accessdeniedexception(messages.getmessage( "abstractaccessdecisionmanager.accessdenied", "access is denied")); } // to get this far, every accessdecisionvoter abstained checkallowifallabstaindecisions();} |
通過以上代碼可直接看到affirmativebased的策略:
- 只要有投通過(access_granted)票,則直接判為通過。
- 如果沒有投通過票且反對(access_denied)票在兩個(gè)及其以上的,則直接判為不通過。
unanimousbased
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
public void decide(authentication authentication, object object, collection<configattribute> attributes) throws accessdeniedexception { int grant = 0; int abstain = 0; list<configattribute> singleattributelist = new arraylist<configattribute>(1); singleattributelist.add(null); for (configattribute attribute : attributes) { singleattributelist.set(0, attribute); for (accessdecisionvoter voter : getdecisionvoters()) { //配置的投票者進(jìn)行投票 int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, singleattributelist); if (logger.isdebugenabled()) { logger.debug("voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result); } switch (result) { case accessdecisionvoter.access_granted: grant++; break; case accessdecisionvoter.access_denied: //只要有投票者投反對票就立馬判為無權(quán)訪問 throw new accessdeniedexception(messages.getmessage( "abstractaccessdecisionmanager.accessdenied", "access is denied")); default: abstain++; break; } } } // to get this far, there were no deny votes if (grant > 0) { //如果沒反對票且有通過票,那么就判為通過 return; } // to get this far, every accessdecisionvoter abstained checkallowifallabstaindecisions();} |
由此可見unanimousbased的策略:
- 無論多少投票者投了多少通過(access_granted)票,只要有反對票(access_denied),那都判為不通過。
- 如果沒有反對票且有投票者投了通過票,那么就判為通過。
consensusbased
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
public void decide(authentication authentication, object object, collection<configattribute> configattributes) throws accessdeniedexception { int grant = 0; int deny = 0; int abstain = 0; for (accessdecisionvoter voter : getdecisionvoters()) { //配置的投票者進(jìn)行投票 int result = voter.vote(authentication, object, configattributes); if (logger.isdebugenabled()) { logger.debug("voter: " + voter + ", returned: " + result); } switch (result) { case accessdecisionvoter.access_granted: grant++; break; case accessdecisionvoter.access_denied: deny++; break; default: abstain++; break; } } if (grant > deny) { //通過的票數(shù)大于反對的票數(shù)則判為通過 return; } if (deny > grant) { //通過的票數(shù)小于反對的票數(shù)則判為不通過 throw new accessdeniedexception(messages.getmessage( "abstractaccessdecisionmanager.accessdenied", "access is denied")); } if ((grant == deny) && (grant != 0)) { //this.allowifequalgranteddenieddecisions默認(rèn)為true //通過的票數(shù)和反對的票數(shù)相等,則可根據(jù)配置allowifequalgranteddenieddecisions進(jìn)行判斷是否通過 if (this.allowifequalgranteddenieddecisions) { return; } else { throw new accessdeniedexception(messages.getmessage( "abstractaccessdecisionmanager.accessdenied", "access is denied")); } } // to get this far, every accessdecisionvoter abstained checkallowifallabstaindecisions();} |
由此可見,consensusbased的策略:
- 通過的票數(shù)大于反對的票數(shù)則判為通過。
- 通過的票數(shù)小于反對的票數(shù)則判為不通過。
- 通過的票數(shù)和反對的票數(shù)相等,則可根據(jù)配置allowifequalgranteddenieddecisions(默認(rèn)為true)進(jìn)行判斷是否通過。
到此,應(yīng)該明白affirmativebased、unanimousbased、consensusbased三者的區(qū)別了吧,spring security默認(rèn)使用的是affirmativebased, 如果有需要,可配置為其它兩個(gè),也可自己去實(shí)現(xiàn)。
投票者
以上accessdecisionmanager的實(shí)現(xiàn)類都只是對權(quán)限(投票)進(jìn)行管理(策略的實(shí)現(xiàn)),具體投票(vote)的邏輯是通過調(diào)用accessdecisionvoter的子類(投票者)的vote方法實(shí)現(xiàn)的。spring security默認(rèn)注冊了rolevoter和authenticatedvoter兩個(gè)投票者。下面來看看其源碼。
accessdecisionmanager
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
boolean supports(configattribute attribute);boolean supports(class<?> clazz);//核心方法,此方法由上面介紹的的accessdecisionmanager調(diào)用,子類實(shí)現(xiàn)此方法進(jìn)行投票。int vote(authentication authentication, s object, collection<configattribute> attributes); |
rolevoter
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
private string roleprefix = "role_";//只處理role_開頭的(可通過配置roleprefix的值進(jìn)行改變)public boolean supports(configattribute attribute) { if ((attribute.getattribute() != null) && attribute.getattribute().startswith(getroleprefix())) { return true; } else { return false; }}public int vote(authentication authentication, object object, collection<configattribute> attributes) { if(authentication == null) { //用戶沒通過認(rèn)證,則投反對票 return access_denied; } int result = access_abstain; //獲取用戶實(shí)際的權(quán)限 collection<? extends grantedauthority> authorities = extractauthorities(authentication); for (configattribute attribute : attributes) { if (this.supports(attribute)) { result = access_denied; // attempt to find a matching granted authority for (grantedauthority authority : authorities) { if (attribute.getattribute().equals(authority.getauthority())) { //權(quán)限匹配則投通過票 return access_granted; } } } } //如果處理過,但沒投通過票,則為反對票,如果沒處理過,那么視為棄權(quán)(access_abstain)。 return result;} |
很簡單吧,同時(shí),我們還可以通過實(shí)現(xiàn)accessdecisionmanager來擴(kuò)展自己的voter。但是,要實(shí)現(xiàn)這個(gè),我們還必須得弄清楚attributes這個(gè)參數(shù)是從哪兒來的,這個(gè)是個(gè)很關(guān)鍵的參數(shù)啊。通過一張官方圖能很清晰的看出這個(gè)問題來:
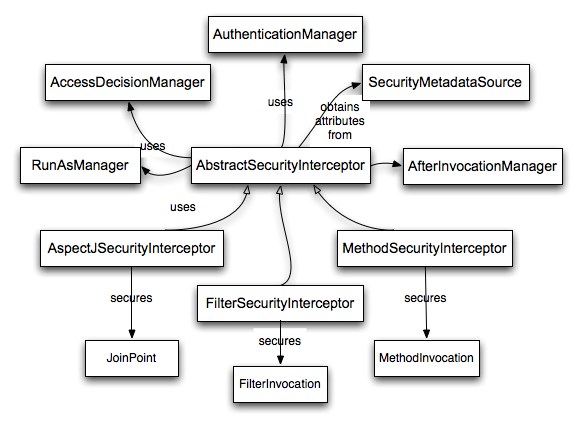
接下來,就看看accessdecisionmanager的調(diào)用者abstractsecurityinterceptor。
abstractsecurityinterceptor
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
...//上面說過默認(rèn)是affirmativebased,可配置private accessdecisionmanager accessdecisionmanager;...protected interceptorstatustoken beforeinvocation(object object) { ... //抽象方法,子類實(shí)現(xiàn),但由此也可看出configattribute是由securitymetadatasource(實(shí)際上,默認(rèn)是defaultfilterinvocationsecuritymetadatasource)獲取。 collection<configattribute> attributes = this.obtainsecuritymetadatasource() .getattributes(object); ... //獲取當(dāng)前認(rèn)證過的用戶信息 authentication authenticated = authenticateifrequired(); try { //調(diào)用accessdecisionmanager this.accessdecisionmanager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes); } catch (accessdeniedexception accessdeniedexception) { publishevent(new authorizationfailureevent(object, attributes, authenticated, accessdeniedexception)); throw accessdeniedexception; } ... }public abstract securitymetadatasource obtainsecuritymetadatasource(); |
以上方法都是由abstractsecurityinterceptor的子類(默認(rèn)是filtersecurityinterceptor)調(diào)用,那就再看看吧:
filtersecurityinterceptor
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
...//securitymetadatasource的實(shí)現(xiàn)類,由此可見,可通過外部配置。這也說明我們可以通過自定義securitymetadatasource的實(shí)現(xiàn)類來擴(kuò)展出自己實(shí)際需要的configattributeprivate filterinvocationsecuritymetadatasource securitymetadatasource; ...//入口public void dofilter(servletrequest request, servletresponse response, filterchain chain) throws ioexception, servletexception { filterinvocation fi = new filterinvocation(request, response, chain); //關(guān)鍵方法 invoke(fi);}public void invoke(filterinvocation fi) throws ioexception, servletexception { if ((fi.getrequest() != null) && (fi.getrequest().getattribute(filter_applied) != null) && observeonceperrequest) { // filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe // once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking fi.getchain().dofilter(fi.getrequest(), fi.getresponse()); } else { // first time this request being called, so perform security checking if (fi.getrequest() != null) { fi.getrequest().setattribute(filter_applied, boolean.true); } //在這兒調(diào)用了父類(abstractsecurityinterceptor)的方法, 也就調(diào)用了accessdecisionmanager interceptorstatustoken token = super.beforeinvocation(fi); try { fi.getchain().dofilter(fi.getrequest(), fi.getresponse()); } finally { super.finallyinvocation(token); } //完了再執(zhí)行(父類的方法),一前一后,aop無處不在啊 super.afterinvocation(token, null); }} |
好啦,到此應(yīng)該對于spring security的權(quán)限管理比較清楚了。看完這個(gè),不知你是否能擴(kuò)展出一套適合自己需求的權(quán)限需求來呢,如果還不太清楚,那也沒關(guān)系,下篇就實(shí)戰(zhàn)一下,根據(jù)它來開發(fā)一套自己的權(quán)限體系。
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家的學(xué)習(xí)有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持服務(wù)器之家。
原文鏈接:http://www.cnblogs.com/dongying/p/6106855.html