歡迎訪問我的GitHub
這里分類和匯總了欣宸的全部原創(chuàng)(含配套源碼):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
本篇概覽
- 本文是《java與es8實戰(zhàn)》系列的第六篇,經(jīng)過前面的實戰(zhàn),咱們初步掌握了一些Java對ES的基本操作,通過發(fā)送請求對象(例如CreateIndexResponse)到ES服務(wù)端,達(dá)到操作ES的目的,但是細(xì)心的您可能發(fā)現(xiàn)了:請求對象可能很復(fù)雜,例如多層對象嵌套,那么用代碼來創(chuàng)建這些請求對象也必然不會容易
- 今天的文章,咱們先來體驗用代碼創(chuàng)建請求對象的不便之處,再嘗試ES官方給我們提供的解決之道:用JSON創(chuàng)建請求對象
- 接下來,咱們從一個假設(shè)的任務(wù)開始
任務(wù)安排
- 現(xiàn)在咱們要創(chuàng)建一個索引,此索引記錄的是商品信息
- 有一個副本(屬于setting部分)
- 共三個分片(屬于setting部分)
- 共三個字段:商品名稱name(keyword),商品描述description(text),價格price(integer)(屬于mapping部分)
- name字段值長為256,超出此長度的字段將不會被索引,但是會存儲
- 接下來,咱們在kibana上用JSON創(chuàng)建索引,再寫代碼創(chuàng)建相同索引,然后對比兩種方式的復(fù)雜程度
kibana上創(chuàng)建索引
- 如果在kibana上用json來創(chuàng)建,請求內(nèi)容如下,索引名是product001
PUT product001
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
},
"description": {
"type": "text"
},
"price": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
- 效果如下,符合預(yù)期
- 通過eshead觀察,也是符合預(yù)期
- 可見基于JSON的操作簡單明了,接下來看看創(chuàng)建相通索引的代碼是什么樣子
基于代碼創(chuàng)建
- 關(guān)于如何連接ES的代碼并非本篇重點,而且前面的文章已有詳細(xì)說明,就不多贅述了
- 首先創(chuàng)建一個API,可以接受外部傳來的Setting和Mapping設(shè)定,然后用這些設(shè)定來創(chuàng)建索引
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient;
@Override
public void create(String name,
Function<IndexSettings.Builder, ObjectBuilder<IndexSettings>> settingFn,
Function<TypeMapping.Builder, ObjectBuilder<TypeMapping>> mappingFn) throws IOException {
elasticsearchClient
.indices()
.create(c -> c
.index(name)
.settings(settingFn)
.mappings(mappingFn)
);
}
- 然后就是如何準(zhǔn)備Setting和Mapping參數(shù),再調(diào)用create方法完成創(chuàng)建,為了讓代碼順利執(zhí)行,我將調(diào)用create方法的代碼寫在單元測試類中,這樣后面只需要執(zhí)行單元測試即可調(diào)用create方法
@SpringBootTest
class EsServiceImplTest {
@Autowired
EsService esService;
@Test
void create() throws Exception {
// 索引名
String indexName = "product002";
// 構(gòu)建setting時,builder用到的lambda
Function<IndexSettings.Builder, ObjectBuilder<IndexSettings>> settingFn = sBuilder -> sBuilder
.index(iBuilder -> iBuilder
// 三個分片
.numberOfShards("3")
// 一個副本
.numberOfReplicas("1")
);
// 新的索引有三個字段,每個字段都有自己的property,這里依次創(chuàng)建
Property keywordProperty = Property.of(pBuilder -> pBuilder.keyword(kBuilder -> kBuilder.ignoreAbove(256)));
Property textProperty = Property.of(pBuilder -> pBuilder.text(tBuilder -> tBuilder));
Property integerProperty = Property.of(pBuilder -> pBuilder.integer(iBuilder -> iBuilder));
// // 構(gòu)建mapping時,builder用到的lambda
Function<TypeMapping.Builder, ObjectBuilder<TypeMapping>> mappingFn = mBuilder -> mBuilder
.properties("name", keywordProperty)
.properties("description", textProperty)
.properties("price", integerProperty);
// 創(chuàng)建索引,并且指定了setting和mapping
esService.create(indexName, settingFn, mappingFn);
}
}
- 由于Java API Client中所有對象都統(tǒng)一使用builder pattern的方式創(chuàng)建,這導(dǎo)致代碼量略多,例如setting部分,除了setting自身要用Lambda表達(dá)式,設(shè)置分片和副本的代碼也要用Lambda的形式傳入,這種嵌套效果在編碼中看起來還是有點繞的,閱讀起來可能會有點不適應(yīng)
- 執(zhí)行單元測試,如下圖,未發(fā)生異常
- 用kibana查看新建的索引
- 最后,將product001和product002的mapping放在一起對比,可見一模一樣
- 再用eshead對比分片和副本的效果,也是一模一樣
小結(jié)和感慨
- 至此,可以得出結(jié)論:
- Java API Client的對ES的操作,能得到kibana+JSON相同的效果
- 然而,用java代碼來實現(xiàn)JSON的嵌套對象的內(nèi)容,代碼的復(fù)雜程度上升,可讀性下降(純屬個人感覺)
- 另外,在開發(fā)期間,我們也常常先用kibana+JSON先做基本的測試和驗證,然后再去編碼
- 因此,如果能在代碼中直接使用kibana的JSON,以此取代復(fù)雜的builder pattern代碼去創(chuàng)建各種增刪改查的請求對象,那該多好啊
- ES官方預(yù)判了我的預(yù)判,在Java API Client中支持使用JSON來構(gòu)建請求對象
能用JSON的根本原因
-
動手實踐之前,有個問題先思考一下
-
剛才咱們寫了那么多代碼,才能創(chuàng)建出CreateIndexResponse對象(注意代碼:elasticsearchClient.indices().create),怎么就能用JSON輕易的創(chuàng)建出來呢?有什么直接證據(jù)或者關(guān)鍵代碼嗎?
-
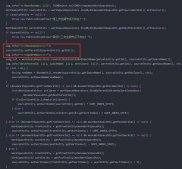
來看看CreateIndexResponse的builder的源碼,集成了父類,也實現(xiàn)了接口,
public static class Builder extends WithJsonObjectBuilderBase<Builder>
implements
ObjectBuilder<CreateIndexRequest> {
- 用IDEA查看類圖的功能,Builder的繼承和實現(xiàn)關(guān)系一目了然,注意紅色箭頭指向的WithJson接口,它是Builder父類實現(xiàn)的接口,也是讓CreateIndexResponse可以通過JSON來創(chuàng)建的關(guān)鍵
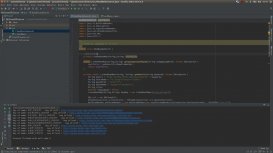
- 強大的IDEA,可以在上圖直接展開WithJson接口的所有方法簽名,如下圖,一目了然,三個方法三種入?yún)ⅲC明了使用者可以用三種方式將JSON內(nèi)容傳給Builder,再由Builer根據(jù)傳入的內(nèi)容生成CreateIndexResponse實例
創(chuàng)建工程
- 在《java與es8實戰(zhàn)之二:實戰(zhàn)前的準(zhǔn)備工作》中創(chuàng)建整了個系列共用的父工程elasticsearch-tutorials,今天新建的新工程名為object-from-json,也屬于elasticsearch-tutorials的子工程,pom.xml如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<!-- 請改為自己項目的parent坐標(biāo) -->
<parent>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-tutorials</artifactId>
<groupId>com.bolingcavalry</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<relativePath>../pom.xml</relativePath>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<!-- 請改為自己項目的artifactId -->
<artifactId>object-from-json</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<!-- 請改為自己項目的name -->
<name>object-from-json</name>
<url>https://github.com/zq2599</url>
<!--不用spring-boot-starter-parent作為parent時的配置-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${springboot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 不加這個,configuration類中,IDEA總會添加一些提示 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<!-- exclude junit 4 -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- junit 5 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- elasticsearch引入依賴 start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>co.elastic.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用spring boot Maven插件時需要添加該依賴 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.json</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.json-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- 需要此插件,在執(zhí)行mvn test命令時才會執(zhí)行單元測試 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-M4</version>
<configuration>
<skipTests>false</skipTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>
- 是個普通的SpringBoot應(yīng)用,入口類FromJsonApplication.java如下,非常簡單
package com.bolingcavalry.fromjson;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class FromJsonApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FromJsonApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 然后是連接ES的配置類ClientConfig.java,關(guān)于如何連接ES,在《java與es8實戰(zhàn)之四》一文已經(jīng)詳細(xì)說明,不再贅述,直接使用配置類的elasticsearchClient方法創(chuàng)建的ElasticsearchClient對象即可操作ES
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "elasticsearch") //配置的前綴
@Configuration
public class ClientConfig {
@Setter
private String hosts;
/**
* 解析配置的字符串,轉(zhuǎn)為HttpHost對象數(shù)組
* @return
*/
private HttpHost[] toHttpHost() {
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(hosts)) {
throw new RuntimeException("invalid elasticsearch configuration");
}
String[] hostArray = hosts.split(",");
HttpHost[] httpHosts = new HttpHost[hostArray.length];
HttpHost httpHost;
for (int i = 0; i < hostArray.length; i++) {
String[] strings = hostArray[i].split(":");
httpHost = new HttpHost(strings[0], Integer.parseInt(strings[1]), "http");
httpHosts[i] = httpHost;
}
return httpHosts;
}
@Bean
public ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient() {
HttpHost[] httpHosts = toHttpHost();
RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder(httpHosts).build();
RestClientTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper());
// And create the API client
return new ElasticsearchClient(transport);
}
}
- 最后是配置文件application.yml
elasticsearch:
# 多個IP逗號隔開
hosts: 127.0.0.1:9200
- 現(xiàn)在工程已經(jīng)建好,接下來開始實踐如何通過JSON得到請求對象,通過剛才對WithJson接口的分析,JSON轉(zhuǎn)請求對象共有三種方式
- ImputStream
- JSON字符串
- Parse
- 接下來逐個實踐
- 開始編碼,首先創(chuàng)建一個接口EsService.java,里面有名為create的方法,這是創(chuàng)建索引用的,入?yún)⑹撬饕桶蠮SON內(nèi)容的InputStream
public interface EsService {
/**
* 以InputStream為入?yún)?chuàng)建索引
* @param name 索引名稱
* @param inputStream 包含JSON內(nèi)容的文件流對象
*/
void create(String name, InputStream inputStream) throws IOException;
}
-
接下來是重點:EsService接口的實現(xiàn)類EsServiceImpl.java,可見非常簡單,只要調(diào)用builder的withJson方法,將InputStream作為入?yún)魅爰纯?/li>
@Service
public class EsServiceImpl implements EsService {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient;
@Override
public void create(String name, InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
// 根據(jù)InputStrea創(chuàng)建請求對象
CreateIndexRequest request = CreateIndexRequest.of(builder -> builder
.index(name)
.withJson(inputStream));
elasticsearchClient.indices().create(request);
}
}
- 為了驗證EsServiceImpl的create方法,先準(zhǔn)備好json文件,文件名為product003.json,完整路徑是:/Users/will/temp/202206/25/product003.json
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
},
"description": {
"type": "text"
},
"price": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
- 最后寫一個單元測試類,調(diào)用EsServiceImpl的create方法,將product003.json轉(zhuǎn)成InputStream對象作為其入?yún)ⅲ炞Ccreate方法的功能是否符合預(yù)期,如下所示,代碼非常簡單
@Test
void createByInputStream() throws Exception {
// 文件名
String filePath = "/Users/will/temp/202206/25/product003.json";
// 索引名
String indexName = "product003";
// 通過InputStream創(chuàng)建索引
esService.create(indexName, new FileInputStream(filePath));
}
- 運行單元測試代碼,一切正常

- 用kibana查看product003索引,如下所示,符合預(yù)期

- 再用eshead查看副本和分片,和之前的兩個索引一致

分析Reader類
- 接下來嘗試WithJson接口的第二個方法
default T withJson(Reader input) {
JsonpMapper mapper = SimpleJsonpMapper.INSTANCE_REJECT_UNKNOWN_FIELDS;
return withJson(mapper.jsonProvider().createParser(input), mapper);
}
- 先來看看這個Reader的繼承關(guān)系,本篇不會詳細(xì)分析Reader代碼,咱們重點關(guān)注它的兩個比較重要的子類:StringReader和FileReader

- 接下來先用FileReader作為withJson方法的入?yún)ⅲ炞C用文件來創(chuàng)建請求對象,再用StringReader作為withJson方法的入?yún)ⅲ炞C用字符串來創(chuàng)建請求對象
/**
* 以Reader為入?yún)?chuàng)建索引
* @param name 索引名稱
* @param reader 包含JSON內(nèi)容的文件流對象
*/
void create(String name, Reader reader) throws IOException;
-
接下來是重點:EsService接口的實現(xiàn)類EsServiceImpl.java,可見非常簡單,只要調(diào)用builder的withJson方法,將Reader作為入?yún)魅爰纯?/li>
@Override
public void create(String name, Reader reader) throws IOException {
// 根據(jù)Reader創(chuàng)建請求對象
CreateIndexRequest request = CreateIndexRequest.of(builder -> builder
.index(name)
.withJson(reader));
elasticsearchClient.indices().create(request);
}
-
json文件繼續(xù)使用剛才創(chuàng)建的product003.json文件
-
單元測試代碼中也增加一個方法,用于驗證剛才寫的create方法
@Test
void createByReader() throws Exception {
// 文件名
String filePath = "/Users/will/temp/202206/25/product003.json";
// 索引名
String indexName = "product004";
// 通過InputStream創(chuàng)建索引
esService.create(indexName, new FileReader(filePath));
}
- 接下來是執(zhí)行單元測試方法,在kibana和eshead上驗證product004索引和之前新建的幾個索引是否一致,這里就不多占用篇幅了,結(jié)論是一模一樣
- 其實吧,用InputStream或者Reader作為參數(shù),內(nèi)部實現(xiàn)是一回事,來看看FileReader構(gòu)造方法的源碼吧,里面是InputStream
public class FileReader extends InputStreamReader {
public FileReader(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException {
super(new FileInputStream(fileName));
}
/**
* 以字符串為入?yún)?chuàng)建索引
* @param name 索引名稱
* @param jsonContent 包含JSON內(nèi)容的字符串
*/
void create(String name, String jsonContent) throws IOException;
-
接下來是重點:EsService接口的實現(xiàn)類EsServiceImpl.java,可見非常簡單,用字符串創(chuàng)建StringReader對象,然后只要調(diào)用builder的withJson方法,將StringReader對象作為入?yún)魅爰纯?/li>
@Override
public void create(String name, String jsonContent) throws IOException {
// 根據(jù)Reader創(chuàng)建請求對象
CreateIndexRequest request = CreateIndexRequest.of(builder -> builder
.index(name)
.withJson(new StringReader(jsonContent)));
elasticsearchClient.indices().create(request);
}
- 為了驗證上面的create方法,在單元測試類中新增一個方法來驗證
@Test
void createByString() throws Exception {
// 文件名
String jsonContent = "{\n" +
" \"settings\": {\n" +
" \"number_of_shards\": 3,\n" +
" \"number_of_replicas\": 1\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"name\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"ignore_above\": 256\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"description\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}\n";
// 索引名
String indexName = "product005";
// 通過InputStream創(chuàng)建索引
esService.create(indexName, jsonContent);
}
- 接下來是執(zhí)行單元測試方法,在kibana和eshead上驗證product004索引和之前新建的幾個索引是否一致,這里就不多占用篇幅了,結(jié)論是一模一樣
T withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper)
- 前面三種方法,咱們都寫了代碼去驗證,不過最后這種就不寫代碼驗證了,原因很簡單:沒必要,咱們先來看看WithJson接口的源碼
public interface WithJson<T> {
default T withJson(InputStream input) {
JsonpMapper mapper = SimpleJsonpMapper.INSTANCE_REJECT_UNKNOWN_FIELDS;
return withJson(mapper.jsonProvider().createParser(input), mapper);
}
default T withJson(Reader input) {
JsonpMapper mapper = SimpleJsonpMapper.INSTANCE_REJECT_UNKNOWN_FIELDS;
return withJson(mapper.jsonProvider().createParser(input), mapper);
}
T withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper);
}
- 可見,前面使用過的withJson(InputStream input)和withJson(Reader input),其實都是在調(diào)用withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper),所以,在實際使用中,掌握withJson(InputStream input)和withJson(Reader input)就已經(jīng)夠用了,如果一定要使用withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper),就參考上面的代碼去構(gòu)造JsonParser即可
代碼和JSON內(nèi)容混用
- 有時候用代碼和JSON混合使用來創(chuàng)建請求對象,既能用JSON省去大量代碼工作,又能用代碼保持該有的靈活性,如下所示,查詢用JSON字符串,聚合參數(shù)用builder的API生成
Reader queryJson = new StringReader(
"{" +
" \"query\": {" +
" \"range\": {" +
" \"@timestamp\": {" +
" \"gt\": \"now-1w\"" +
" }" +
" }" +
" }" +
"}");
SearchRequest aggRequest = SearchRequest.of(b -> b
.withJson(queryJson)
.aggregations("max-cpu", a1 -> a1
.dateHistogram(h -> h
.field("@timestamp")
.calendarInterval(CalendarInterval.Hour)
)
.aggregations("max", a2 -> a2
.max(m -> m.field("host.cpu.usage"))
)
)
.size(0)
);
Map<String, Aggregate> aggs = client
.search(aggRequest, Void.class)
.aggregations();
- 另外,不光是請求對象,與請求對象有關(guān)的實例也能用JSON生成,回顧本文最開始的那段代碼中,構(gòu)造CreateIndexResponse對象時還要創(chuàng)建Property對象,實際上這個Property是可以通過JSON生成的,參考代碼如下
String json = "{ " +
" \"type\": \"text\"," +
" \"fields\": {" +
" \"some_field\": { " +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"," +
" \"normalizer\": \"lowercase\"" +
" }" +
" }" +
" }";
Property p = Property.of(b -> b
.withJson(new StringReader(json))
);
- 至此,基于JSON構(gòu)造ES請求對象的實戰(zhàn)就完成了,今后在kibana上驗證通過的JSON請求體,可以直接放在代碼中用于使用,這將有效的降低代碼量,也提升了整體可讀性
源碼下載
- 本篇實戰(zhàn)的完整源碼可在GitHub下載到,地址和鏈接信息如下表所示(https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos)
public interface EsService {
/**
* 以InputStream為入?yún)?chuàng)建索引
* @param name 索引名稱
* @param inputStream 包含JSON內(nèi)容的文件流對象
*/
void create(String name, InputStream inputStream) throws IOException;
}
@Service
public class EsServiceImpl implements EsService {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient;
@Override
public void create(String name, InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
// 根據(jù)InputStrea創(chuàng)建請求對象
CreateIndexRequest request = CreateIndexRequest.of(builder -> builder
.index(name)
.withJson(inputStream));
elasticsearchClient.indices().create(request);
}
}
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
},
"description": {
"type": "text"
},
"price": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
@Test
void createByInputStream() throws Exception {
// 文件名
String filePath = "/Users/will/temp/202206/25/product003.json";
// 索引名
String indexName = "product003";
// 通過InputStream創(chuàng)建索引
esService.create(indexName, new FileInputStream(filePath));
}
default T withJson(Reader input) {
JsonpMapper mapper = SimpleJsonpMapper.INSTANCE_REJECT_UNKNOWN_FIELDS;
return withJson(mapper.jsonProvider().createParser(input), mapper);
}
- 接下來是重點:EsService接口的實現(xiàn)類EsServiceImpl.java,可見非常簡單,只要調(diào)用builder的withJson方法,將Reader作為入?yún)魅爰纯?/li>
@Override
public void create(String name, Reader reader) throws IOException {
// 根據(jù)Reader創(chuàng)建請求對象
CreateIndexRequest request = CreateIndexRequest.of(builder -> builder
.index(name)
.withJson(reader));
elasticsearchClient.indices().create(request);
}
-
json文件繼續(xù)使用剛才創(chuàng)建的product003.json文件
-
單元測試代碼中也增加一個方法,用于驗證剛才寫的create方法
@Test
void createByReader() throws Exception {
// 文件名
String filePath = "/Users/will/temp/202206/25/product003.json";
// 索引名
String indexName = "product004";
// 通過InputStream創(chuàng)建索引
esService.create(indexName, new FileReader(filePath));
}
- 接下來是執(zhí)行單元測試方法,在kibana和eshead上驗證product004索引和之前新建的幾個索引是否一致,這里就不多占用篇幅了,結(jié)論是一模一樣
- 其實吧,用InputStream或者Reader作為參數(shù),內(nèi)部實現(xiàn)是一回事,來看看FileReader構(gòu)造方法的源碼吧,里面是InputStream
public class FileReader extends InputStreamReader {
public FileReader(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException {
super(new FileInputStream(fileName));
}
/**
* 以字符串為入?yún)?chuàng)建索引
* @param name 索引名稱
* @param jsonContent 包含JSON內(nèi)容的字符串
*/
void create(String name, String jsonContent) throws IOException;
-
接下來是重點:EsService接口的實現(xiàn)類EsServiceImpl.java,可見非常簡單,用字符串創(chuàng)建StringReader對象,然后只要調(diào)用builder的withJson方法,將StringReader對象作為入?yún)魅爰纯?/li>
@Override
public void create(String name, String jsonContent) throws IOException {
// 根據(jù)Reader創(chuàng)建請求對象
CreateIndexRequest request = CreateIndexRequest.of(builder -> builder
.index(name)
.withJson(new StringReader(jsonContent)));
elasticsearchClient.indices().create(request);
}
- 為了驗證上面的create方法,在單元測試類中新增一個方法來驗證
@Test
void createByString() throws Exception {
// 文件名
String jsonContent = "{\n" +
" \"settings\": {\n" +
" \"number_of_shards\": 3,\n" +
" \"number_of_replicas\": 1\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"name\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"ignore_above\": 256\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"description\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}\n";
// 索引名
String indexName = "product005";
// 通過InputStream創(chuàng)建索引
esService.create(indexName, jsonContent);
}
- 接下來是執(zhí)行單元測試方法,在kibana和eshead上驗證product004索引和之前新建的幾個索引是否一致,這里就不多占用篇幅了,結(jié)論是一模一樣
T withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper)
- 前面三種方法,咱們都寫了代碼去驗證,不過最后這種就不寫代碼驗證了,原因很簡單:沒必要,咱們先來看看WithJson接口的源碼
public interface WithJson<T> {
default T withJson(InputStream input) {
JsonpMapper mapper = SimpleJsonpMapper.INSTANCE_REJECT_UNKNOWN_FIELDS;
return withJson(mapper.jsonProvider().createParser(input), mapper);
}
default T withJson(Reader input) {
JsonpMapper mapper = SimpleJsonpMapper.INSTANCE_REJECT_UNKNOWN_FIELDS;
return withJson(mapper.jsonProvider().createParser(input), mapper);
}
T withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper);
}
- 可見,前面使用過的withJson(InputStream input)和withJson(Reader input),其實都是在調(diào)用withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper),所以,在實際使用中,掌握withJson(InputStream input)和withJson(Reader input)就已經(jīng)夠用了,如果一定要使用withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper),就參考上面的代碼去構(gòu)造JsonParser即可
代碼和JSON內(nèi)容混用
- 有時候用代碼和JSON混合使用來創(chuàng)建請求對象,既能用JSON省去大量代碼工作,又能用代碼保持該有的靈活性,如下所示,查詢用JSON字符串,聚合參數(shù)用builder的API生成
Reader queryJson = new StringReader(
"{" +
" \"query\": {" +
" \"range\": {" +
" \"@timestamp\": {" +
" \"gt\": \"now-1w\"" +
" }" +
" }" +
" }" +
"}");
SearchRequest aggRequest = SearchRequest.of(b -> b
.withJson(queryJson)
.aggregations("max-cpu", a1 -> a1
.dateHistogram(h -> h
.field("@timestamp")
.calendarInterval(CalendarInterval.Hour)
)
.aggregations("max", a2 -> a2
.max(m -> m.field("host.cpu.usage"))
)
)
.size(0)
);
Map<String, Aggregate> aggs = client
.search(aggRequest, Void.class)
.aggregations();
- 另外,不光是請求對象,與請求對象有關(guān)的實例也能用JSON生成,回顧本文最開始的那段代碼中,構(gòu)造CreateIndexResponse對象時還要創(chuàng)建Property對象,實際上這個Property是可以通過JSON生成的,參考代碼如下
String json = "{ " +
" \"type\": \"text\"," +
" \"fields\": {" +
" \"some_field\": { " +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"," +
" \"normalizer\": \"lowercase\"" +
" }" +
" }" +
" }";
Property p = Property.of(b -> b
.withJson(new StringReader(json))
);
- 至此,基于JSON構(gòu)造ES請求對象的實戰(zhàn)就完成了,今后在kibana上驗證通過的JSON請求體,可以直接放在代碼中用于使用,這將有效的降低代碼量,也提升了整體可讀性
源碼下載
- 本篇實戰(zhàn)的完整源碼可在GitHub下載到,地址和鏈接信息如下表所示(https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos)
@Override
public void create(String name, String jsonContent) throws IOException {
// 根據(jù)Reader創(chuàng)建請求對象
CreateIndexRequest request = CreateIndexRequest.of(builder -> builder
.index(name)
.withJson(new StringReader(jsonContent)));
elasticsearchClient.indices().create(request);
}
@Test
void createByString() throws Exception {
// 文件名
String jsonContent = "{\n" +
" \"settings\": {\n" +
" \"number_of_shards\": 3,\n" +
" \"number_of_replicas\": 1\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"name\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"ignore_above\": 256\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"description\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}\n";
// 索引名
String indexName = "product005";
// 通過InputStream創(chuàng)建索引
esService.create(indexName, jsonContent);
}
- 前面三種方法,咱們都寫了代碼去驗證,不過最后這種就不寫代碼驗證了,原因很簡單:沒必要,咱們先來看看WithJson接口的源碼
public interface WithJson<T> {
default T withJson(InputStream input) {
JsonpMapper mapper = SimpleJsonpMapper.INSTANCE_REJECT_UNKNOWN_FIELDS;
return withJson(mapper.jsonProvider().createParser(input), mapper);
}
default T withJson(Reader input) {
JsonpMapper mapper = SimpleJsonpMapper.INSTANCE_REJECT_UNKNOWN_FIELDS;
return withJson(mapper.jsonProvider().createParser(input), mapper);
}
T withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper);
}
- 可見,前面使用過的withJson(InputStream input)和withJson(Reader input),其實都是在調(diào)用withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper),所以,在實際使用中,掌握withJson(InputStream input)和withJson(Reader input)就已經(jīng)夠用了,如果一定要使用withJson(JsonParser parser, JsonpMapper mapper),就參考上面的代碼去構(gòu)造JsonParser即可
代碼和JSON內(nèi)容混用
- 有時候用代碼和JSON混合使用來創(chuàng)建請求對象,既能用JSON省去大量代碼工作,又能用代碼保持該有的靈活性,如下所示,查詢用JSON字符串,聚合參數(shù)用builder的API生成
Reader queryJson = new StringReader(
"{" +
" \"query\": {" +
" \"range\": {" +
" \"@timestamp\": {" +
" \"gt\": \"now-1w\"" +
" }" +
" }" +
" }" +
"}");
SearchRequest aggRequest = SearchRequest.of(b -> b
.withJson(queryJson)
.aggregations("max-cpu", a1 -> a1
.dateHistogram(h -> h
.field("@timestamp")
.calendarInterval(CalendarInterval.Hour)
)
.aggregations("max", a2 -> a2
.max(m -> m.field("host.cpu.usage"))
)
)
.size(0)
);
Map<String, Aggregate> aggs = client
.search(aggRequest, Void.class)
.aggregations();
- 另外,不光是請求對象,與請求對象有關(guān)的實例也能用JSON生成,回顧本文最開始的那段代碼中,構(gòu)造CreateIndexResponse對象時還要創(chuàng)建Property對象,實際上這個Property是可以通過JSON生成的,參考代碼如下
String json = "{ " +
" \"type\": \"text\"," +
" \"fields\": {" +
" \"some_field\": { " +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"," +
" \"normalizer\": \"lowercase\"" +
" }" +
" }" +
" }";
Property p = Property.of(b -> b
.withJson(new StringReader(json))
);
- 至此,基于JSON構(gòu)造ES請求對象的實戰(zhàn)就完成了,今后在kibana上驗證通過的JSON請求體,可以直接放在代碼中用于使用,這將有效的降低代碼量,也提升了整體可讀性
源碼下載
- 本篇實戰(zhàn)的完整源碼可在GitHub下載到,地址和鏈接信息如下表所示(https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos)
| 名稱 | 鏈接 | 備注 |
|---|---|---|
| 項目主頁 | https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos | 該項目在GitHub上的主頁 |
| git倉庫地址(https) | https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos.git | 該項目源碼的倉庫地址,https協(xié)議 |
| git倉庫地址(ssh) | [email protected]:zq2599/blog_demos.git | 該項目源碼的倉庫地址,ssh協(xié)議 |
- 這個git項目中有多個文件夾,本次實戰(zhàn)的源碼在elasticsearch-tutorials文件夾下,如下圖紅框
- elasticsearch-tutorials是個父工程,里面有多個module,本篇實戰(zhàn)的module是object-from-json,如下圖紅框
歡迎關(guān)注博客園:程序員欣宸
學(xué)習(xí)路上,你不孤單,欣宸原創(chuàng)一路相伴...